Oligonucleotide Formulations Prepared by High-Speed Electrospinning: Maximizing Loading and Exploring Downstream Processability
today’s cyclodextrin:
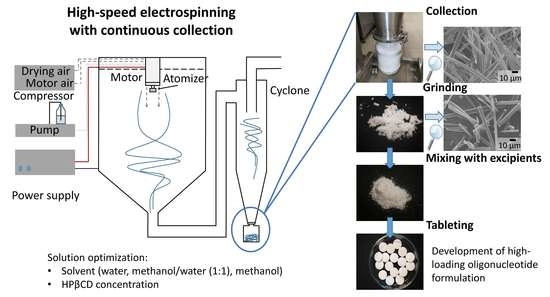
is about developing antisense oligonucleotide tablet formulations using high-speed electrospinning. Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) was used as a stabilizer and an electrospinning matrix from one of the best pharma groups in Hungary (FirePharma Research Group BME – Budapest University of Technology and Economics) collaborating with Janssen Inc.
The fibrous HPβCD–antisense oligonucleotide formulations showed no sign of physical or chemical degradation over the 1-year stability study, which also shows the suitability of the HPβCD matrix for the formulation of biopharmaceuticals. The obtained results demonstrate possible solutions for the challenges of electrospinning, such as scale-up and downstream processing of the fibers.
Edit Hirsch, Márió Nacsa, Edina Szabó, Panna Vass, Julia Domjan, Attila Farkas,Zsuzsanna Eke, Tamás Vigh, Sune Klint Andersen, Geert Verreck, György Marosi and Zsombor Kristof Nagy et al
See the full article here: Oligonucleotide Formulations Prepared by High-Speed Electrospinning: Maximizing Loading and Exploring Downstream Processability