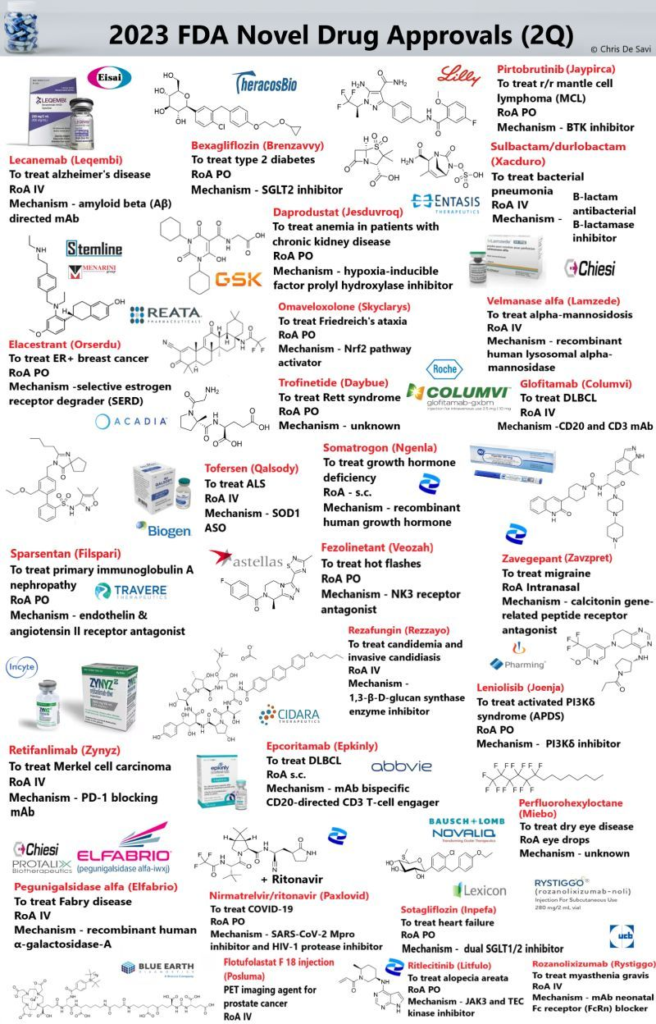
US FDA grants standard approval of Eisai/Biogen Alzheimer’s drug
Eisai and Biogen’s Leqembi won a coveted standard approval nod from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on Thursday, the first Alzheimer’s treatment to achieve that goal, clearing the way for wider insurance coverage of the drug.
The FDA decision marks a new milestone for a fatal disease that has eluded drugmakers’ efforts for decades. Trial data showed that the treatment slows the progression of the brain-wasting disease by 27% for patients in the earliest stages of Alzheimer’s.
The FDA also placed its strongest “boxed” safety warning on Leqembi’s label, flagging the risk of potentially dangerous brain swelling for Alzheimer’s drugs in the same class.
Leqembi is an antibody designed to remove sticky deposits of a protein called amyloid beta from the brains of Alzheimer’s patients.
Leqembi received “accelerated” FDA approval in January based on its amyloid-clearing ability, but the U.S. government’s Medicare health plan for people aged 65 and over had restricted coverage only to patients in a clinical trial.
Standard approval means that Leqembi will now be covered, although the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) is linking reimbursement to patient participation in a health agency database, known as a registry. Since Alzheimer’s is a disease of aging, most U.S. patients are insured by Medicare.
The official announcement is on reuters.com!